Acer saccharum – Scientific classification
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Sapindales |
| Family: | Sapindaceae |
| Genus: | Acer |
| Species: |
A. saccharum
|

Characteristics
Sugar maple (Acer saccharum Marshall) is a deciduous tree from the Sapindaceae family. It grows to 30 m in height, the canopy is thick and oval. The bark is brownish-gray and almost smooth at a young age, later having long and irregular furrows. Young branches are brown, covered with warty lenticels. The pups are the opposite. The leaves are opposite, as wide as long, cut into 3-5 irregular, slightly serrated lobes, dark green on the face, brighter in the fall, turning red in autumn, long petioles, without white milky juice. The flowers are yellowish-green, small, hanging on a 3-7 cm long petiole, appearing simultaneously with leafing. The fruit is about 2-3 cm long-winged feathers in pairs, ripens in autumn.
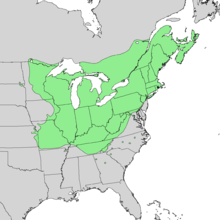
Habitat – Range
It is widespread in the North and Central North America. It is grown as an ornamental tree, suited to a lot of light and fertile, deep and fresh soil. His life span is over 400 years. It blooms after 10 years.
Etymology
The Latin name for the genus Acer is the old Latin name for maple, meaning sharp, pointed, because of the leaves of pointed lobes. The name of the Saccharum species indicates that it contains sugar.

Use
From the tree is collected the juice used to produce maple syrup. The trees can be used for more than 100 years, with annual yields of 12-35 kg of sugar. It takes 40 liters of juice to produce 1 liter of syrup.
Wood is used to make furniture, sometimes it has interesting patterns for unknown reasons but for which it is especially appreciated.


Pingback: Acer obtusatum - Forestry Book
Pingback: Acer tataricum-Tatar maple - Forestry Book